Author: Falak Baqar
Introduction
Fundamentally, climate change is the term used to describe long-term changes in Earth’s weather and temperatures (United Nations., n.d.). Although the climate may be affected by natural phenomena like volcanic eruptions and variations in the sun’s energy, the present emphasis is on human-induced climate change, which is mostly caused by activities like burning fossil fuels (including petroleum, natural gas, and coal), destruction of forests, and manufacturing activities. The World Bank Group (2023) indicates that by 2050, climate change may force 216 million people to leave their home nations, with internal migration hubs commencing as early as 2030 and then expanding and accelerating later.
Climate change has gained popularity recently, but what does it really imply and why should we care?
Unveiling the Catalysts and Consequences of Climate Transformation
Catalysts
- According to NASA (2023), deforestation has recently been considered the primary cause of substantial climate change in recent eras. When trees are cut down or burnt, the carbon they contain is released as CO2 into the atmosphere. Additionally, trees are essential for absorbing CO2, hence their disappearance results in higher levels of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
- Another cause of climate change is found to be agricultural issues. UNEP (2023) explored that methane and nitrous oxide, both powerful greenhouse gases, are released as a result of agricultural operations, such as animal production and the use of synthetic fertilizers. These gases are massively attacking the environment, resulting in a climatic change that can be adverse for people; mainly those living in underprivileged areas. For example, ethnic minorities residing in the area of Africa and Asia where access to facilities is little to zero are observed to be influenced by sudden alterations in the climate; especially children and women (Mthuli, 2022).
- Moreover, NASA (2023) investigated that several greenhouse gases are being emitted from industrial as well as manufacturing practices, including perfluorocarbons (PFCs) and hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs). These gases play a role in increasing the potential of global warming thus, affecting the overall climate.
- Notwithstanding this fact, the United Nations (2022) focused on the fact that urban heat islands and other localized warming effects are brought on by urbanization and changes in land use, which also affect the Earth’s surface’s ability to reflect sunlight.
Consequences
- Global temperatures are rising, which is causing heatwaves to occur more frequently and with greater severity. For agriculture, ecology, and human health, this might have disastrous effects (UNEP, 2023).
- By looking at recent news by BBC World (2023), polar ice caps and glaciers are melting due to rising temperatures, which is causing sea levels to increase. Coastal flooding results from this, endangering coastal populations and resulting in saltwater intrusion into freshwater sources.
- Climate change makes extreme weather events like hurricanes, droughts, wildfires, and torrential rains that cause floods and landslides more often and intense.
- Climate and weather changes disturb ecosystems and put plant and animal species in danger. Many species might have difficulty adapting or could become extinct.
- Crop yields are impacted by climate change, which also decreases some regions’ water supply and raises the possibility of food and water shortages, which has an influence on food security worldwide. As per BBC News (2023), the UK government claims that fieldwork can provide energy for the population to benefit, whereas, criticism has been raised against the government, calling it an ‘environmental vandalism’ that is negatively affecting their food and water.
- As temperatures rise, heat-related illnesses can develop as well as the development of infections brought by insects like mosquitoes. Stress brought on by the environment is also a worry for mental health.
- Dealing with weather-related calamities, property damage, and the impact on sectors like insurance, tourism, and agriculture all have high economic costs.
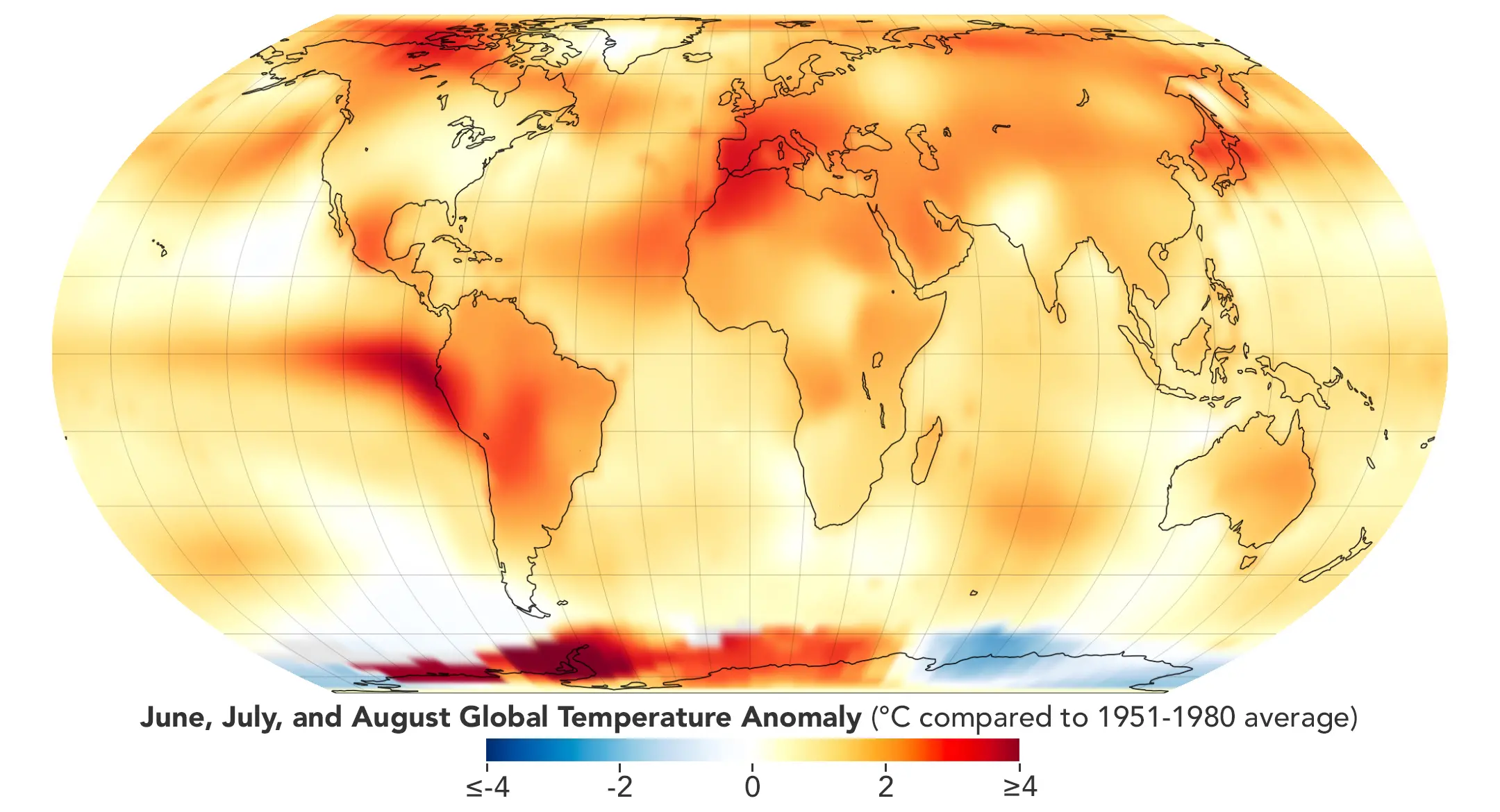
Why Should We Be Concerned?
There is no place on Earth that is immune to the effects of climate change. Here’s why this matters;
Temperature increases pose a threat to human health and cause inconveniences in everyday life. Heat waves may be deadly, particularly for the elderly and the young. The effects of climate change on the economy may be significant. Insurance premium increases, property damage, and lost jobs in affected sectors might all have a significant financial effect. Climate change threatens our capacity to provide for ourselves by reducing agricultural output and increasing water shortages. Regional instability and global insecurity may result from climate-related conflicts, resource shortages, and population relocation. We owe it to future generations to act against climate change now so that they can inherit a habitable planet.
Conclusion
Climate change is an urgent and significant global issue that has widespread implications for all individuals. The resolution of this issue does not just rest upon future generations but rather needs immediate action. Gaining a comprehensive understanding of the fundamental principles and implementing incremental changes in one’s everyday routine to minimize their ecological impact might cumulatively provide substantial outcomes. Climate change is a pervasive worldwide concern that originates from the decisions and behaviors of human actors. Let us collaborate in order to secure a future that is both healthier and more sustainable for present and future generations.
